1. Instrument Flying under IFR
There are four segments for an instrument flying under IFR and each segment has specific procedures
a) Departure
b) En route
c) Arrival
d) Approach

2. Instrument Departure Procedures (DPs): SIDs& ODPs [AIM 5-2-8]
- pre-planned IFR procedures
- provide obstruction clearance from the terminal area to the appropriate en route structure,
- provide the pilot with a way to depart the airport and transition to the en route structure safely.
DPs 에 대해서 설명할 때는 High way 진입에 대해서 많이 설명한다. 이런저런 작은 LOCAL driving 이후 High way 입구까지 보내는 역할과 비슷하다고 할 수 있다.
There are 4 departure options
1) Graphic DP (SIDs and ODPs)
: Can be a portion of IFR clearance
2) Textural DP (Obstacle DPs, ODPs)
- Not assigned as a portion of IFR clearance(But, in IMC, DP is only way to obstacle clearance)
- May be flown without ATC clearance

위 두 가지가 메인인데, DP를 보게 되면 그림이 그려진 것도 있고 그렇지 않고 글만으로 설명된 것 들이 있다.
3) Radar Vector Departure
4) VFR Departure (Depart airport under VFR obtaining clearance from ARTCC)
※ No DP: 만약 DP를 통한 Departure- Enroute 진입을 하고 싶지 않으면 Flight plan 에 기입할 수 있다.
(1) Standard Instrument Departure Procedures (SIDs)
What is this?
: Take us from the terminal area safely to a fix in the en-route system
Why do we use this?
- Primary reason is to reduce radio congestion and workload and obstruction clearance
: 이의 경우 단어사용과 비슷하다. 한 단어는 여러가지 의미를 포함할 수 있는데, 이처럼 한 번에 계속해서 의미를 설명하는 것 보다, 한 단어를 사용하면서 라디오사용을 줄일 수 있게 된다. 그리고 Instrument chart의 경우 거의 대부분 장애물을 피할 수 있게 하게 된다. 이는 VFR을 할 수 없을 때를 위한 목적이 크기 때문에 그것을 기준으로 해서 고도설정이나 Route 설정을 더 하기 때문에 그렇다.
- So it usually has only in airports with heavy IFR flights such as KPHX
- Simplify ATC clearance (SIDs are generally long routes)
- ATC clearance must be received before flying a SID
- Might be multiple SIDs per airport
- Always printed textual and praphically
: 이는 필요도를 생각하면 된다. 보통 흔히 사용되지 않는 공항의 경우 쓸데없이 돈을 들여 graphically 만들 필요가 없다. 그러나 SID가 있는 정도의 공항은 사용빈도가 크다. 그렇기 때문에 편의를 위해서 더 만들게 된다.
(a)How do we use this?
- All pilot are encouraged to file and fly a DP at night, in VMC/ IMC when one is available
- The pilot must ensure the DP requirements can be met (Departure Standards)
- Requires pilot possession of the text/ graphic depiction of the approved, current DP
- RNAV SIDs must be conformed to the charted procedure
(b) SID responsibilities
> ATC
- Responsible for specifying the direction of T/O or initial heading when necessary
- Procedure complies with local traffic patterns, terrain, and obstruction clearance
- Including the DP as part of the ATC clearance
> Pilot
- Acknowledgement and understanding of an ATC clearance
- Read back any part of a clearance that contains "hold short" instructions
- Request clarification of clearances
- Request an amendment to a clearance if it is unacceptable from a safety perspective
- Promptly comply with ATC requests (advise immediately if unable
(c) Clearance
- "Cleared for '___' departure" (Lateral clearance only)
- "Climb via '___' departure" (Lateral and vertical clearance)
eg) Cessna 2464D, proceed direct RAISN, climb via the PRYME TWO Departure.
- Direct RAISN, climb via the PRYME two departure
What is climb via?
- it is to reduce phraseology by eliminating the need for the controller to restate restrictions at the remaining way point
- it is a clearance to navigate laterally and vertically
Why is it important?
: When you are vectored off the published routing (usually by ATC), and are issued instruction direct to a waypoint on the SIDs
※ Top altitude
- ATC may assign a top altitude or an altitude that is different from the published top altitude
- So, we cannot climb more than top altitude while SIDs unless getting clearance
이건, Climb 중일 때가 큰데 특정 고도까지 올라 가다가 '일단 그만 올라가고 일정 고도를 유지하고 있어!' 라는 느낌이 있다. 다른 비행기가 지나갈 수 있기 때문에 사고를 막기 위하여 할 수도 있다. 또 10,000 ft 가 미니멈일 경우 그 이후로 고도변경이 가능할 경우도 이 이상은 올라오지마 위험할 수 있어 라는 느낌이 있다.
| ODPs | SIDs |
| - Obstacle Clearance - No concern about efficiency - One procedure per airport - Only where IFR airport with an obstacle - No need clearance | - Obstacle clearance - Increase efficiency/ reduce ATC comm. - At busy IFR airport - Multiple SIDs per airport - Must obtain clearance |
(2) Obstacle Departure Procedures (ODPs)
What is ODPs?
: It is one of the DPs provided with graphically or textually to the pilot
What is the purpose of ODPs?
- ODPs may be flown without ATC clearance unless an alternate departure procedure has been specifically assigned by ATC
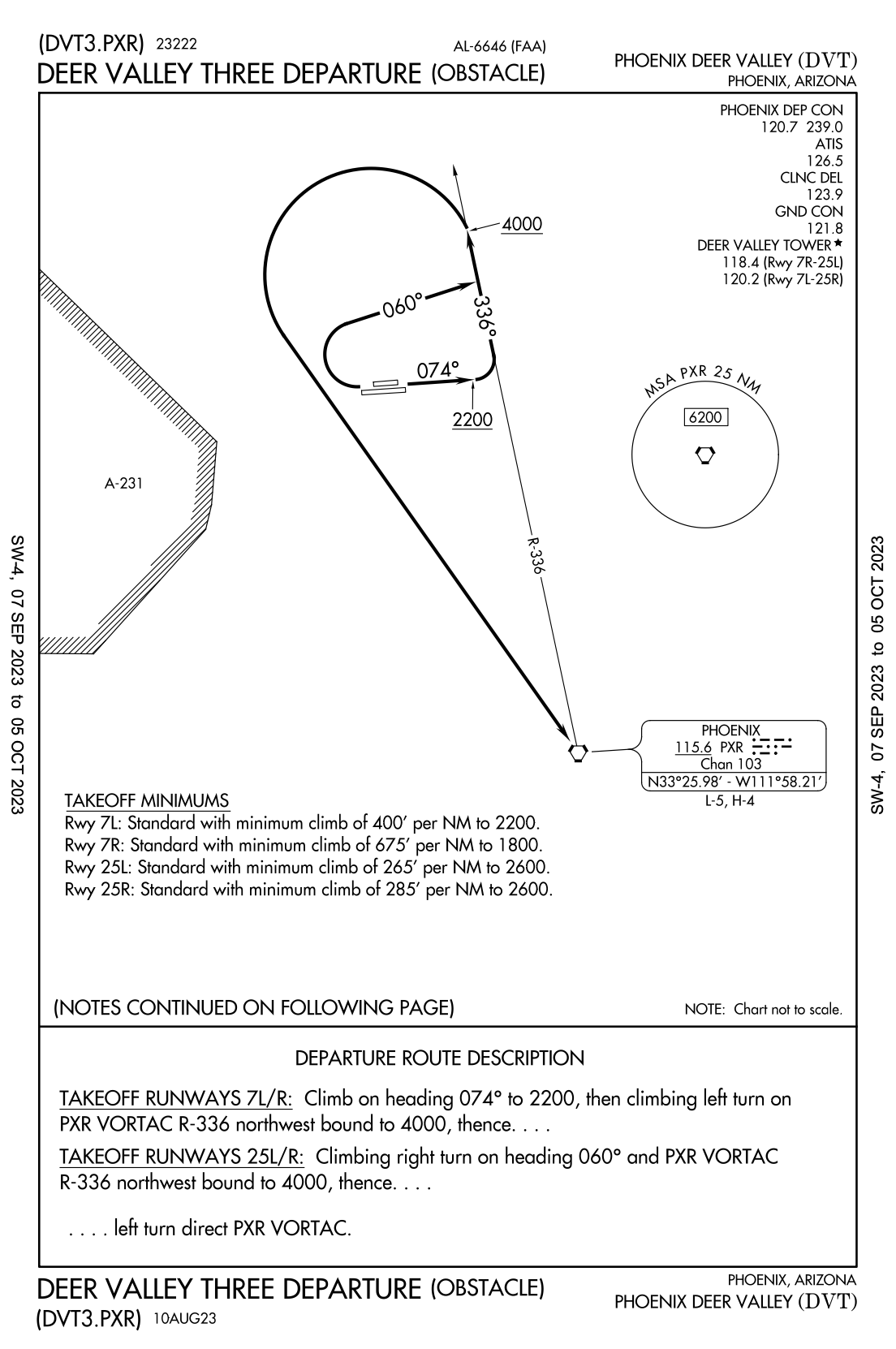
eg) Deervalley One Departure (Obstable)

- Designed specifically to provide obstacle clearance during the climb from the terminal area to the en-route structure
- Least onerous (easiest) route from the airport to a fix in the enroute system
- Pilots (Part 91) are strongly encouraged to fly published DPs at night, in marginal VMC and in IMC to ensure obstacle clearance
- Usually only one ODP per airport in textual form (some are graphical)
- Pilot must have at least the textual form to fly the procedure
How do DPs develop?
- When an instrument approach is initially developed for an airport, the need for DPs is assessed
- The procedure designer conducts an obstacle analysis to support departure operations
- If an obstacle penetrates what is called a '40:1 obstacle identification surface (OIS)', then the procedure designer chooses whether to
a) Establish a steeper-than-normal climb gradient
(※ The Standard climb gradient is 200FPNM)
b) Establish a steeper than normal climb gradient with an alternative that increases takeoff minima to allow the pilot to visually remain clear of the obstacles, or
(※ Take off minimum is 1 SM (1-2 engine), ½ SM (3 or more engines)
이것은 Part 91 을 위한 것은 아니다. Part 91 을 위하여는 정해진 Take off minimum 이 없다. 이 말은 아무때나 비행할 수있지만, 위험한 비행을 허락하지 않는다. 그렇기 때문에 Personal minimum을 사용하게 된다. 이 때 그래도 최소한 이정도는 되어야 한다 라는 의미로 이것을 많이 사용하게 된다.)
c) Design and publish a specific departure route to follow
d) Decrease takeoff runway distance
Take off 를 미리 하게 되면 일정 위치에서 더 높은 Altitude를 얻을 수 있기 때문이다.
(※ GRAND THREE DEPARTURE - KGCN; 아 이게 지금(10/4/23은 사라졌구나...)
Criteria to provide ODPs [AIM 5-2-8, b]
https://airresearch.com/Pilots/AIM-08/Chap5/aim0502.html
AIM - Chapter 5, Section 2
5-2-1. Pre-taxi Clearance Procedures a. Certain airports have established pre-taxi clearance programs whereby pilots of departing instrument flight rules (IFR) aircraft may elect to receive their IFR clearances before they start taxiing for takeoff. The fo
airresearch.com
- It is based on the pilot crossing the departure end of the runway (DER) elevation, climbing to 400 feet above the DET elevation before making the initial turn, and maintaining a mimimum climb gradient of 200 FPNM.
- If an initial turn higher than 400 feet above the DER is specified in DP, the turn should be commenced at the higher altitude. If it is a fix, turn at the fix which may have MCA.
Why is the ODP published?
- So, if the obstacle that is located within 1NM of the DER and penetrates 40:1 OCS is referred to as a "low, close-in obstacle". The standard Required Obstacle Clearance (ROC) of 48 F/NM to clear an obstacle would require a climb gradient greater than 200 F/NM.
- To eliminate publishing an excessive climb gradient, the obstacle AGL height and location relative to the DER is noted in the "take-off minimum" section.
- If the obstacle breaks the 152 F/NM (40:1) plane (line) until 25 NM (non-mountainous area)/ 46 NM (mountainous area)
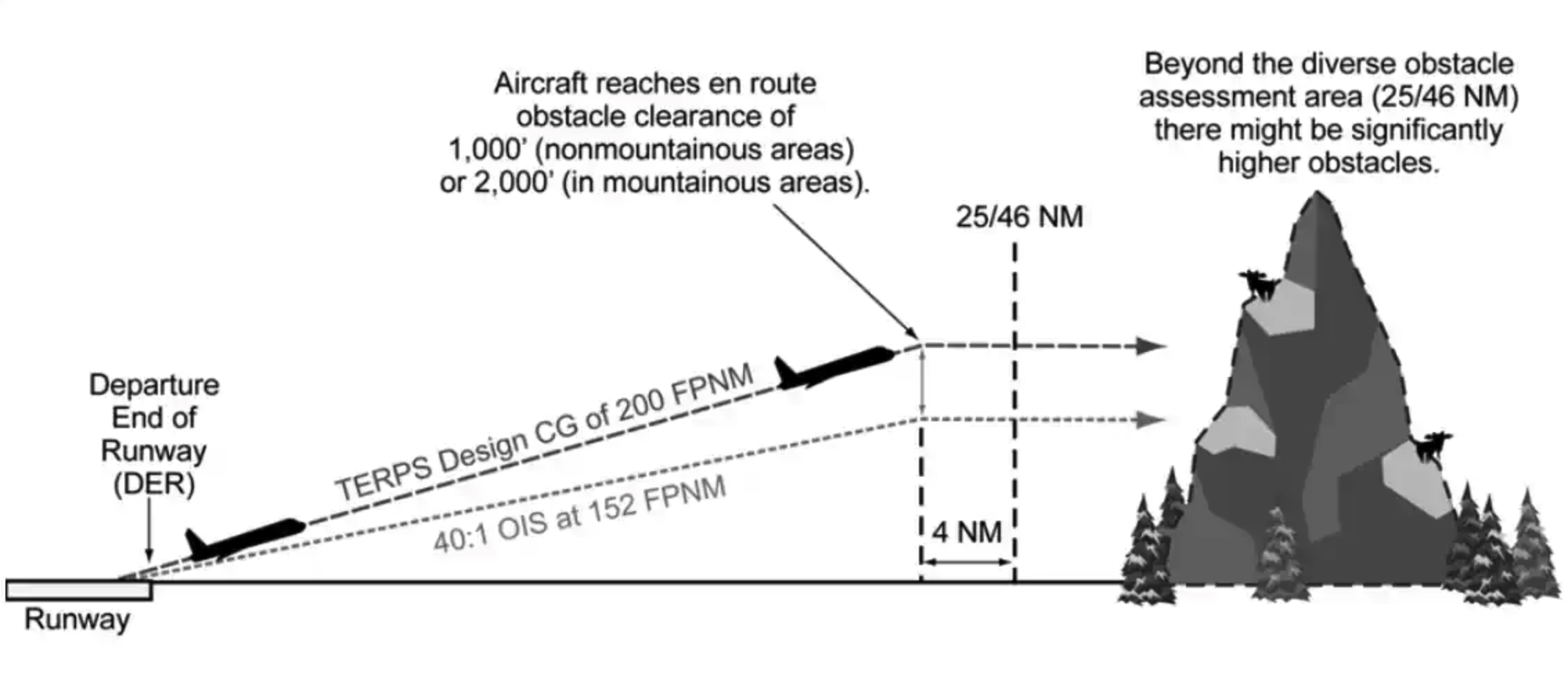
Three things to meet before the turn (AIM 5-2-8)
a) cross DER at or above 35 feet
b) climb above 400 feet AGL
c) minimum of 200 F/NM climb gradient
*When radar is vectored, fly heading without wind correction.
Where can I find that information?
- To eliminate published an excessive climb gradient, the obstacle AGL height and location relation to the DER is noted in the "Take-off minimums" and "Departure procedures" section
*Standard Take-off minimum (for airliner, charter or scheduled flight)
1-2 Engine: 1 SM
3- or more: ½ SM
As a FAR 91 operator, not required to operate but comply with the landing minimum for safety.
How?
Uses personal takeoff minimums
eg) do not takeoff below the departure airport "landing minimums in approach plate"
How to fly ODP? (IFH 1-12, AIM 5-2-8(3))
- If DP requires a higher than standard climb gradient, we must determine of out aircraft can achieve that climb gradient
1) Crosse DER above 35 feet AGL
2) Climb to 400 Feet above airport elevation before turning (Maintain heading till 400 Feet AGL)
*Lowest altitude for any IFR departure is 400 Feet AGL
3) Climb at least 200 FPNM (that's 300 FPM at ground speed: 90 Knots) or higher gradient specified in DP to assigned altitude
* GS(90)/ 60 * 200 FPNM= 300 FPM
eg) Deer Valley One Departure, with below condition, can we takeoff?
Cloud: 900 Feet OVC/ Weight: 2,400 LBS/ Temp 35 ℃/ Altimeter setting: 29.92 inHg/ RWY: 7R/ Visibility: 2NM/ Wind: No
Takeoff minimum (7R)
a) 500-1 1/4 with a minimum climb of 488 FPNM to 2,800 Feet
b) 1500-3 for climb in visual conditions
How do we calculate?
- Visibility is less than 3 SM, we cannot take off because it's IMC conditions
- So, we use "74 (GS)/60 * 488 (FPNM)= 601 FPM"
- Open PIM 5-17 to check the maximum rate of climb (FPM)
- Under those conditions, get the pressure altitude, then get the rate of climb is 635 FPM
- If PIM tells rate of climb is lower than 601 FPM, we cannot clear the obstacle
- So, the Maximum rate of climb (PIM) must be higher than the current required FPM to clear obstacles.
How can I file for DVT 1 departure?
- (DVT1. PXR): This code you're going to use when filing a flight plan when you want to use the DVT1 departure.
- (Obstacle): It indicates it is ODP.
VCOA: Visual Climb Over Airport
- Climb in visual conditions to cross over airport at a certain altitude before proceeding on course
- To ensure safe and efficient operations, the pilot must verbally request approval from ATC to fly the VCOA when requesting their IFR clearance
- If NO takeoff minimums and climb gradient are shown, use the standard figure.
Diverse Vector Area
- ATC provides course guidance during a departure procedure using radar vector. Allows ATC to vector you below the normal minimum vectoring altitude (It might have non-standard climb gradients)
- At some locations where ODP has been established, a DVA may be created to allow radar vectors to be used in lieu of ODP. DVA information will state that headings will be assigned by ATC and climb gradients.
3. Pilot NAV DP and Vector DP
: Obstacle graphic DPs (ODPs) and SIDs are one of two types, either Pilot NAV or Vector
> Pilot NAV DPs
- Designed to allow to navigate along a specific route with minimal ATC communications
- Have an initial set of instruction (one or more transition routes)
- Basic Procedure/ Transition/ Minimum Crossing Altitudes/ Minimum Climb Rate
> Vector DPs
- Established where ATC provides radar navigation guidance
- Similar to pilot NAV DPs but no 'departure route' and no 'transition'
- Basic procedure/ Minimum Climb Rate/ Lost Communication
'✈ 비행과 공부 > CFII' 카테고리의 다른 글
| FAA Medical exam (appointment) (0) | 2023.10.10 |
|---|---|
| Departure Procedures (2) | 2023.10.10 |
| Preflight preparation_ Task C: Instrument Cockpit Check (0) | 2023.09.28 |
| Task D_ Logbook Entries Related to Instrument Instruction (0) | 2023.09.27 |
| Instrument Rating Requirement(3/3) (0) | 2023.09.25 |




댓글